
Some of these are still in operation today, but they have been extensively upgraded. They had a higher output, around 800 megawatts (roughly the power consumption of a large city), reinforced containment and multiple after-cooling and emergency cooling systems. There were numerous improvements with second-generation reactors. The goal of all these improvements is an inherently safe system – protection by natural laws against a meltdown, accidents or human error. Today the nuclear power plants of this generation are all shut down and for the most part, dismantled.

These “2-out-of-3” systems are used in all complex technologies (aviation, high-speed trains, railway control, space travel). This means that if two out of three measured variables deviate, countermeasures are taken. In the 1950s, first-generation nuclear technology already included a containment to protect against accidents, emergency cooling systems and triple parallel electronic control and safety systems. For comparison, a 1000-megawatt reactor generates per year roughly the amount of power needed to supply the city of Vienna. At that time, plants still had an electrical output of 300 megawatts. The first generation of nuclear power plants was mostly built between 1955 and the late 1960s. support to build their own nuclear infrastructure. Knowledge about nuclear fission had previously been kept secret, but it was released after the speech and several countries received U.S. Nuclear energy began to spread in earnest after the 1953 “Atoms for Peace” speech by United States President Dwight Eisenhower. To make the technology even safer, over the last decades engineers have been working to create new reactor designs that are more efficient and, in some cases, can even be powered with radioactive waste. For nuclear energy, this figure is only 0.07 deaths. Nevertheless, skepticism toward nuclear energy is often much greater.įor every terawatt-hour of energy generated (roughly the annual electricity consumption of 27,000 people in the European Union) there are 32.72 deaths due to accidents and air pollution associated with lignite. This is especially true compared to fossil fuels. There is a similar inconsistency with nuclear energy: despite public fears, when measured in terms of deaths per amount of electricity, it is one of the safest and cleanest energy sources.
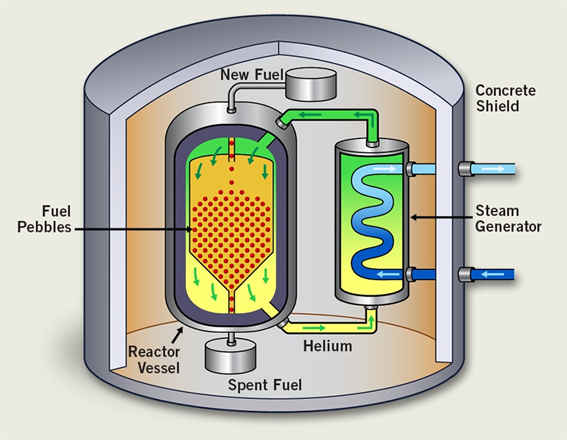
More preparatory work is needed to implement the newest technologiesįor most people flying is scarier than driving a car, even if the latter has been shown to be more dangerous.Recent innovations could make accidents virtually impossible.Nuclear power has been continually improving since its beginnings.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
